Output of the results
The coordinates of the polygon and the mapped polygons are output for each mapping of the chain.
Use the button  in the toolbar to create a report with the results and the graph.
in the toolbar to create a report with the results and the graph.
Example 1:
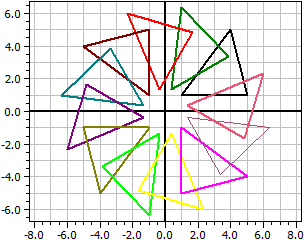
Original polygon A(1|1), B(5|1), C(5|5), D(3|7), E(1|5), 1. Translation: dx=2, dy=1 ☑ A(3|2), B(7|2), C(7|6), D(5|8), E(3|6), 2. Rotation: Z(2|-1), α=-60° ☑ A(5,0981|-0,36603), B(7,0981|-3,8301), C(10,562|-1,8301), D(11,294|0,90192), E(8,5622|1,634),
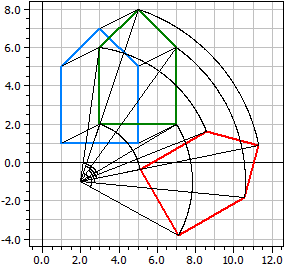
Example 2:
Multiple mappings of the same type are also possible. So you can also apply multiple symmetrys on different axis to the polygon.
Original polygon A(1|1), B(5|1), C(4|5), 1. Axial symmetry: a=(PQ), P(0|0), Q(1|1) A(1|1), B(1|5), C(5|4), 2. Axial symmetry: a=(PQ), P(0|0), Q(0|1) A(-1|1), B(-1|5), C(-5|4), 3. Axial symmetry: a=(PQ), P(0|0), Q(-1|1) A(-1|1), B(-5|1), C(-4|5), 4. Axial symmetry: a=(PQ), P(0|0), Q(0|1) A(-1|-1), B(-5|-1), C(-4|-5), ...
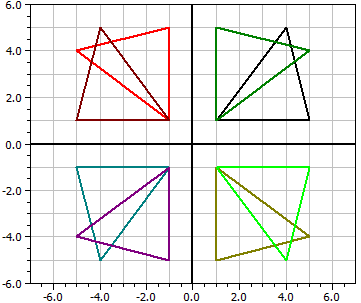
Example 3:
Original polygon A(1|1), B(5|1), C(4|5), 1. Rotation: Z(0|0), α=30° A(0.366|1.37), B(3.83|3.37), C(0.964|6.33), 2. Rotation: Z(0|0), α=30° A(-0.366|1.37), B(1.63|4.83), C(-2.33|5.96), 3. Rotation: Z (0/0), α=30° A(-1|1), B(-1|5), C(-5|4), ...