Newton-Iteration
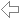
Newton's iteration is an approximation method for the calculating a zero of ƒ(x). Given an initial value x0 that is close enough to the desired zero, the next approximation is the intersection of the tangent to the graph of ƒ in the point P(x0|ƒ(x0)) with the x-axis.
This gives the recursion formula
The procedure converges, if ƒ(x0) · ƒ "(x0)>0
is valid for x0.
Example:
ƒ(x) = x-cos(x)
x ƒ(x) ƒ'(x)
———————— —————— ——————
x0 = 1
x1 = 0,75036387 0,45969769 1,841471
x2 = 0,73911289 0,018923074 1,681905
x3 = 0,73908513 0,00004646 1,6736325
x4 = 0,73908513 0,00000000 1,673612
See also:
Supported FunctionsWikipedia: Newton's method