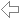
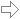
Intersection of two Planes
Given two planes the program computes the line of intersection, the line's distance from the origin and the angle of intersection between the two planes.
The planes may be entered in parametric representation or as coordinate equation
The program plots the intersection of the planes in a cube symmetric to the axis and the line of intersection of the two planes.
Example 1:
Given the two planes:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
E1 : 5·x - 2·y = 5
E2 : 2·x - y + 5·z = 8
Intersection line:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
-> ⎧-11 ⎫ ⎧ 10 ⎫
g : x = ⎪-30 ⎪ + r·⎪ 25 ⎪
⎩ 0 ⎭ ⎩ 1 ⎭
Distance from origin:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
d = 1,5057283
Intersection angle:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
alpha = 65,993637°
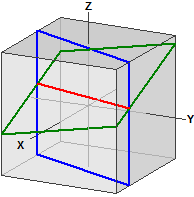
Example 2: Parallel planes
Given the two planes: ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ E1 : 2·x - y + 5·z = 12 E2 : 2·x - y + 5·z = 0 The planes are parallel ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ d(E1,E2) = 2,1908902
The diagram can be rotated with the left mouse button and be zoomed with the right mouse button.