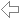
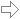
Intersection of Plane and Line
Given a plane and a line, the intersection point and the intersection angle are calculated.
The plane may be entered in parametric representation or as coordinate equation, the line in parametric representation or by two points.
Example 1:
Plane E :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
E : x + y + z = 5
Line g :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
-> ⎧ 5 ⎫ ⎧ 0 ⎫
g : x = ⎪ 0 ⎪ + r·⎪ 1 ⎪
⎩ 0 ⎭ ⎩ 1 ⎭
Intersection point :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
S(5|0|0)
Intersection angle :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
α = 54,73561°
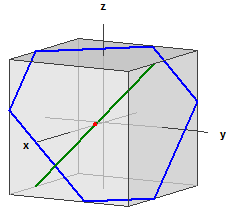
Example 2:
Plane E :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
E : 2·x + 8·y − 5·z = 0
Line g :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
-> ⎧ 2 ⎫ ⎧ 1 ⎫
g : x = ⎪ 0 ⎪ + r·⎪ 1 ⎪
⎩ 3 ⎭ ⎩ 2 ⎭
E and g are parallel
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
d(g,E) = -1,1406469
The diagram can be rotated with the left mouse button and be zoomed with the right mouse button.