Binomial Distribution
For a b(k;n;p) distributed random variable X with fixed n and p you can compute
- a histogram of the probabilities P( X = k )
- a table of their values from kmin to kmax
- the probability P( kmin < X < kmax)
Theory:
n balls are randomly drawn from a container containing a proportion p of red balls. The random
variable X stands for the number of red balls drawn. The probability that k of the balls drawn are red,
is given by
The values for n and p are entered, where p must be between 0 and 1. Then a simple histogram gives a first overview
of the values of
Example:
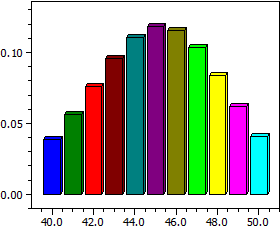
n = 60; p = .75
k P(X=k) P(0 ≤ X < k)
—— —————— ——————
40 0,03834033 0,09248427
41 0,05610780 0,14859207
42 0,07614630 0,22473838
43 0,09562559 0,32036397
44 0,11083875 0,43120273
45 0,11822800 0,54943073
46 0,11565783 0,66508856
47 0,10335381 0,76844237
48 0,08397497 0,85241733
49 0,06169589 0,91411323
50 0,04071929 0,95483252
—— —————— ——————
P(40 ≤ k < 50) = 0,90068858