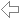
Distances on the sphere
The distance between two points P1 and P2 on a sphere is calculated by combining some functions of MatheAss.
The GPS data (latitude and longitude) of the two points are entered. Together with the radius of the sphere, they give the polar coordinates of the points.
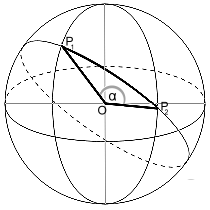
These are converted into their cartesian coordinates with the corresponding function of MatheAss. The result supplies the coordinates of their position vectors in a coordinate system with the center of the sphere as the origin.
Their scalar product gives the angle α between the two vectors and finally the product of α in radians and the radius of the sphere gives the length of the arc on the sphere.
Example:
The distance between Alexanderplatz in Berlin and City Hall in New York.
The Earth is idealized as a sphere with a radius of 6371 km.
GPS decimal
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Berlin : 52.523403, 13.411400
New York : 40.714268, -74.005974
GPS dms
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Berlin : 52°31'24.2508"N, 13°24'41.0400"E
New York : 40°42'51.3648"N, 74° 0'21.5064"W
Polar coordinates
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Berlin : (6371 | 13.411400° | 52.523403°)
New York : (6371 |-74,005974° | 40,714268°)
Cartesian coordinates
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Berlin : (3770.6450 | 899.08721 | 5056.0379)
New York : (1330,5796 |-4642,1091 | 4155,7216)
Position vectors
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
-> ⎧ 3770,645048 ⎫ -> ⎧ 1330,57957098 ⎫
a = ⎪ 899,087213119 ⎪ b = ⎪-4642,10910614 ⎪
⎩ 5056.03788605 ⎭ ⎩ 4155.72160425 ⎭
-> ->
α = arccos( a · b / r2 )
= 1,002215 [rad] = 57,422692°
Distance
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
d = r · α [rad] = 6385,112
Entering GPS data
GPS data can be entered in decimal degrees as well as in degrees, minutes and seconds.
Both representations are output.

The program is therefore also suitable for converting decimal degrees into degrees, minutes and seconds (dms) and vice versa.